Who regulates GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice)? Who conducts GMP audits?
Answer: Regulatory Authorities vary from country to country.
Examples of Regulatory Authorities overseeing the pharmaceutical and/or medical device manufacturing sectors include the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA), the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in the EU, and the MHRA in the United Kingdom (UK).
List of Global Regulatory Authorities
Regulatory Authorities auditing GMP compliance in the manufacture of pharmaceutical products, biologicals, & medical devices.
The manufacture and distribution of therapeutic goods is a highly regulated industry. That’s because the use of such products has the potential to lead to significant public health harms, including serious disability or death.
Good manufacturing practice (GMP) is the critical standard that Regulatory Authorities around the world refer to during regulatory compliance inspections (GMP audits) and other inspections of pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities.
Other standards also generally apply. These may include ISPE guidance/ISPE standards, ISO standards, and the US FDA’s Computer Software Assurance (CSA) expectations, such as outlined in the CSA guidance document the FDA published on 13 September 2022.

Which agencies conduct GMP inspections (GMP audits)?
List of Regulatory Authorities (Regulators) auditing GMP compliance of manufacturers of pharmaceutical products, biologicals, and medical devices.
- Review the list of Regulatory Agencies (known as ‘Pharmaceutical Industry Regulators’ or ‘GMP Inspectors/GMP Auditors’) below.
- Some of the Regulatory Authorities overseeing pharmaceutical manufacturers conduct GMP compliance audits using their own employees.
- Other Regulators may use approved 3rd party GMP inspectors (or expect the manufacturer to engage in externally conducted compliance audits).
- These Audits need to be fully documented, including actions taken to correct any GMP audit findings or other quality issues identified during an inspection, investigation, or other quality incident.
List of Regulatory Authorities (Key Examples)
Regulatory Agencies in different countries include (but are not limited to) the following government agencies/regulatory bodies:
- Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA)
- Malaysian National Pharmaceutical Control Bureau (NPCB)
- Singapore’s Health Sciences Authority (HSA)
- South African Medicines Control Council (MCC)
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (US FDA)
- Canadian Health Products and Food Branch Inspectorate (HPFBI)
- New Zealand’s Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority (Medsafe)
- United Kingdom’s Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA)
- Other Regulatory Authorities (full list of PIC/S members)
How many countries/regulators are participating members of PIC/S?
- There are currently 56 participating PIC/S Authorities.
- To search for PIC/S Members (Regulatory Authorities), click here.
For the full list of participating countries in PIC/S (the Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-Operation Scheme), visit the PIC/S website at https://picscheme.org/en/members.
Learn what a GMP compliance check (GMP audit) really means and which Regulatory Authorities may be auditing your manufacturing organisation or distribution arms for GMP/cGMP compliance & related controls (e.g. cross-contamination controls, distribution controls to prevent falsified medicines from entering supply chains).
This blog article is part of the GMP Basic Training/GMP online training series of articles.
You may also want to explore How to Prepare for an upcoming AUDIT and ensure you and your team undertake adequate GMP compliance training courses.
Brief Overview of Regulatory Authorities in GMP Industries
Regulatory Authorities (RAs) use highly-trained inspectors (RA representatives) to:
- Monitor manufacturing practices (and safety, efficacy and other quality standards) for medicinal products distributed in their regions
- Conduct GMP audits (GMP compliance inspections (onsite and remote inspections)
- Make recommendations and/or issue citations to ensure product quality, safety, & efficacy to protect patients/consumers and hospital medical teams
Regulatory Authorities:
- Have the power to issue citations/fines, demand a product recall, and/or close a facility
- Are responsible for marketing authorisation approvals and GMP clearance certificates in pharmaceutical manufacturing, medical devices manufacturing, blood and tissue products, ATMPs, biological medicines, and other life science industries
- Regulate notification requirements when an adverse event or other ‘drug safety signal’ is discovered by the manufacturer, prescribing physician, hospital team, patient, or other public health/patient stakeholder
We will also discuss the important role of Regulatory Authorities/Regulatory Agencies who are responsible for monitoring GMP (PIC/S) compliance in various regions across the globe.
GMP Audit FAQs: How and when is compliance with GMP rules being monitored (audited)?
GMP compliance by manufacturers/distributors is monitored by:
- Conducting self-inspections (e.g. ‘internal audits’ conducted by the Quality Department and/or 3rd party Inspectors/GMP Auditors)
- Participating in GMP audits conducted by Regulatory Authorities (or their representatives or approved 3rd party GMP Inspectors)
- Generally scheduled audits, with unscheduled inspections where warranted by quality concerns)
- Supplier approvals (Supplier qualification programs/Supplier management practices) including supplier site inspections/GMP audits of your contract holders/intermediate suppliers or other contract organisations involved in producing, storing, and/or distributing the pharmaceutical product(s)

When and how often do GMP compliance audits occur?
The question of ‘when does a Regulatory Authority such as the TGA or FDA conduct GMP audits/site inspections?’ will vary depending on numerous factors.
Factors relating to audit schedules (upcoming audit notifications) and/or unexpected/unannounced GMP compliance audits by Regulators include, but are not limited to:
- Risks of the product(s) being manufactured (example: opioids/fentanyl product risks/overdose risks)
- Prior audit findings (company history/company reputation, past quality-related incidents, GMP breaches, SAEs, etc.)
- Prior warning letters [FDA warning letters] and product recalls
- Reliability of data in the organisation (data integrity requirements in the pharmaceutical industry)
Regulatory Authorities (List)
- You’ll have heard of several of these regulatory agencies already — or at least their commonly used acronyms, such as the FDA, TGA, MHRA, EMA and others.
- But you might not know what they are exactly responsible for in terms of manufacturing safety and public health safety — including GMP audits and PIC/S compliance.
So we’ll cover which authorities monitor quality and safety in pharmaceutical industries — and why GMP compliance audits are important to public health and safety.
This article will be particularly helpful if you also undertake some of our best GMP training options and online GMP courses, and/or blend them with onsite & instructor-led 1-Day GMP training courses (worldwide availability, some of which are live-streamed and others scheduled throughout the year).
Regulatory Authorities & GMP Audits
Regulatory Authorities (RAs) who audit GMP compliance in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing, Medical Devices, Bio-medicines, Veterinary Medicines and other Life Sciences
Whether you’re new to the medical sciences/life science industries and GMP/EU GMP requirements — or have been long employed in the pharmaceutical sector — you’ll need to have formal GMP orientation training.
You’ll also need to regularly refresh your GMP and PIC/S knowledge through online courses and/or onsite training courses.
So, too, will the Management team/business owners, Contractors, Supervisors, Colleagues, Vendors and Suppliers.
Why is GMP compliance training so important?
Ongoing GMP training and development helps your organisation meet recognised quality and safety standards; and assists with product quality assurance, sterility and safety testing. GMP training is also a crucial part of GMP compliance.
From GMP training certificates to self-inspection to CAPA to validation across the lifecycle, from hygiene to cleanroom validation and sterility testing, there are many areas where pharmaceutical or medical device manufacturers can fail a cGMP / EU GMP (PIC/S) audit. Employee GMP training and refresher courses are also regularly reviewed in GMP and PIC/S compliance audits, and are crucial for both GMP compliance and quality management.
If your organisation has an upcoming GMP audit, requires CAPA guidance, or recently failed an FDA or other GMP audit (or you need equipment validation or GMP training for your team), contact PharmOut, the international GMP consultancy experts for bio-sciences and pharmaceutical production.
This article is part of the GMP Orientation Training Blog Series for beginners.
Other GMP guidance articles that support best-practice GMP training programs can be found here.
Introduction to GMP | International Manufacturing Standards

Good manufacturing practices (or ‘GMP’ for short) are required quality management practices in manufacturing sectors.
Regulated manufacturing sectors that must abide by GMP include pharmaceutical production businesses, medical device manufacturers, veterinary medicines manufacturers/suppliers, and other industries that have a significant impact on public health and safety. The aim of GMP is to reduce the risks of a contaminated or otherwise harmful product being given to a patient and to reduce the risks of recalls.
High-risk industries that manufacture pharmaceutical products have the potential to cause serious public health harms. These industries are heavily regulated by Government Authorities (audited for GMP compliance and adequate managerial oversight/risk management). These industries are frequently audited by Regulatory Authorities such as the TGA, FDA, MHRA and EMA. Organisations in these sectors can be cited and fined, completely closed down, and/or forced to recall product batches if there are serious gaps in GMP compliance. Negligence of management oversight of risk controls and personnel training and supervision can even lead to criminal charges instigated by the Authorities. Owners who fail to comply with GMP — and who place patient well-being and public health at risk of serious harms — can be sent to jail.
GMP Compliance Inspections
GMP Audits by Regulatory Authorities

Regulatory authorities like the FDA and TGA regularly inspect pharmaceutical manufacturers and medical device manufacturers and audit their GMP compliance.
Regulators perform these GMP audits in order to protect public health and safety.
- Regulatory agencies are responsible for medication/drug approvals including quality controls auditing of manufacturers and distribution channels.
- These agencies monitor an organization’s compliance to international quality management standards, including risk management systems, documentation practices and data integrity concerns (e.g., GMP compliance, PIC/S compliance).
Each country has a unique agency and/or several government agencies who hold responsibility for ensuring pharmaceutical supply safety; including approving medications for domestic use, research purposes, importation and/or exportation.
The tenets of good manufacturing practices (GMP) relate primarily to:
- Standardisation of product quality (consistency, efficacy, shelf-life, manufacturing practices)
- Assurance of product safety (sterility, content consistency/active ingredients, lack of contaminants)
- Good documentation practices/Good Recordkeeping Practices (GDocP or GRK) as a crucial part of assessing quality controls, testing reports and more
All of the above are part of a larger quality management and risk management approach to manufacturing.
The aim of meeting GMP (and ISO 9001) quality standards is to ensure adherence to a higher level of quality standards that help reduce safety risks to consumers/end-users, patients and others who use these products or systems.
For a list of online GMP training courses, including the 10 golden rules of GMP, click here.
Some aspects you’ll hear spoken of regarding GMP compliance include:
- batch traceability
- good recordkeeping
- sterile processing laboratories
- climate-controlled facilities
- validation schedules
- computer system validation (CSV)
- quality assurance testing at various stages of manufacturing and final product batches
- labelling/packaging
- cleanroom engineering
- secure data systems/data integrity
- aspects of quality testing, facility security, and training procedures
- deviation handling (CAPA – corrective actions and preventive actions) and deviation investigations
Good manufacturing practices, then, govern everything from your initial facility architecture and cleanroom engineering designs to every test procedure/measurement result, reporting system, and records processing system used in the production of therapeutic products and medicines. It starts well before the raw materials (APIs or active pharmaceutical ingredients) are ordered/delivered, and it continues through distribution to the pharmacy/distributor. GMP continues even after the patient receives the medicine, and pharmacovigilance systems (complaints and adverse effects) are closely monitored during GMP compliance audits.
Data integrity, validation (including tamper-proof record-keeping), storage and transportation processes are all governed by GMP…and so much more.
Putting GMP into perspective
You can learn more about GMP by taking our online courses, which provide a GMP Course – Certificate of Completion if you successfully pass the online Final Assessment included in the training module. GMP training courses – click here.
- Standards | Current GMP and PIC/S operational standards (SOPs) are key components in pharmaceutical manufacturing
- ISO9001-2015 is another international standard and there are industry-specific ISO certifications that may also apply
Your organization’s GMP and EU GMP compliance, including SOPs and workflows, must follow current GMP guidelines (“cGMP”) and all must be thoroughly documented and validated.
- If it isn’t written down (recorded in real-time), according to good documentation practices (or GDocP), it didn’t happen.
- Regular self-inspections, validation across the lifecycle of products, validation of your equipment and processes; along with a thoroughly designed and properly implemented CAPA system for investigating — and remedying — deviations in manufacturing, are crucial steps for avoiding a GMP audit failure or facility shut-down due to product safety or processing integrity issues.
How is GMP part of the pharmaceutical and medical devices manufacturing industry?
In brief, good manufacturing practices (GMP) in the pharmaceuticals and other bio-medical-sciences involve the following components:
- safety and quality assurance standards
- risk-minimisation processes
- manufacturing controls including prevention of cross-contamination
- quality testing and reporting throughout the production process as well as the final product or device
- pharmaceutical product distribution rules and batch traceability records
- Source: 10 Golden Rules of GMP (online course)
Quality and Safety in brief for medical and pharmaceutical manufacturing industries: GMP engineering and cGMP (GxP) compliance helps reduce public safety risks by controlling, and continually improving, quality management systems in manufacturing and distribution processes.
CGMP compliance improves product quality and reliability (pharmaceutical production consistency), sustaining regulated safety standards and protecting public health and safety.
The risks of GMP breaches can be serious. Substandard medications or contaminated products can be fatal.

GMP Engineering and Processing | Which parts of pharmaceutical production is GMP involved in?
- GMP is multi-faceted; it involves every aspect of production, including facilities, processes, systems and personnel
- Quality, sterility and testing are engineered into facility designs, HVAC systems, water systems and WIs/SOPs.
- These include designing cleanrooms and other sterile production facilities, monitoring worker gowning and other hygiene according to specific SOPs, maintaining tamper-proof data systems, packaging methods and labelling processes, and ensuring proper employee GMP training incorporating a variety of learning methods
Which businesses are subject to GMP and GMP audits?
- All manufacturing industries should implement GMP, but some regions vary in their degree of GMP auditing or quality-and-safety-testing
- In bio-medicine, GMP applies to pharmaceutical manufacturing, medical device manufacturing, biomedicine production, veterinary medicine production and other therapeutic goods, including approved herbal supplements, complementary medicines and/or medicinal cannabis and other production
The primary aim of GMP compliance — and of conducting GMP or PIC/S audits — is to reduce public safety issues arising from pharmaceuticals and other therapeutic goods. Although it may be monitored by separate agencies, GMP also applies to other industries, e.g. food and beverage manufacturing, cosmetic manufacturing and chemical production.
Bioscience, Medical Devices and Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Risks
Pharmaceutical manufacturing risks include, but are not limited to:
- the risk of substandard medicines or contaminated pharmaceuticals
- risks of falsified documents
- the risks of biohazards and/or exposure to carcinogenic matter (cross-contamination)
- the risks of defects and/or cross-contamination in medical devices or medicines, that could cause adverse reactions (health harms and/or fatalities)
Who conducts GMP audits in pharmaceutical manufacturing, the medical devices industry and biomedicines manufacturing?
Which regulatory agencies have responsibility for GMP audits?
Depending on where your organisation is located and what you’re manufacturing, one of the first questions you’ll have about GMP compliance and training, is which regulatory body governs your workplace and industry?
Which agency conducts GMP audits of your facility, systems, SOPs and personnel? And how often do they audit?
We list some of the industry’s most familiar manufacturing regulatory agencies further in this article.
FAQ: which Government agencies are responsible for assessing safety risks in relation to the manufacturing of pharmaceutical products, medical devices and biomedicines?
The answer depends on which country you’re living in and what you’re making. However, if your product is required to be produced in an entirely sterile environment, with adequate quality-assurance testing and validated cleanroom/engineering, your organisation is likely going to experience frequent regulatory agency audits, to help protect public health and safety.
How they relate to industry employees:
- You’ll be hearing the words GMP compliance, record-keeping accuracy and data integrity, cleanroom validation and GMP auditors (or PIC/S auditing) quite a bit
- If your company hasn’t been complying with GMP precisely, and/or if your colleagues aren’t properly trained and monitored for compliance and GMP knowledge (including CAPA), chances are you’ll be hearing those words stated with a tone of panic
The fact is that GMP audits happen regularly in this industry. They need to occur regularly and frequently, in order to keep the public safe.
- If your organisation isn’t compliant, you could fail an audit
- Significant penalties, batch recalls and/or facility closures could apply
- Some GMP failures could also result in legal actions, lawsuits and/or prosecution
So before or just after you start your online GMP courses, industry-specific GMP training bundles or onsite GMP training (worldwide), let’s discuss WHO actually conducts the PIC/S and GMP audits for your sector.
GMP Basics (a brief overview of what GMP means): If an item (a medicine, supplement or device) is stated as having a therapeutic benefit, it will first need to have gained approval as a therapeutic good for marketing and distribution in your country — and/or for exportation overseas. These pharmaceutical product approvals need to come from particular government agencies, global or regional Regulatory agencies (listed below).
Application processes can be lengthy. That’s because these regulatory agencies have a responsibility to ensure public health and safety, including preventing dangerous, harmful or ineffective products to be made available to the public.
Once a product or medicine is approved as a therapeutic good, then:
- The medicine, supplement or device falls under particular safety-based manufacturing and distribution legislation
- Production is required to meet GMP and/or PIC/S (PIC/S is a specific GMP standard for the pharmaceutical manufacturing industry, discussed below)
- Audits are likely, including investigations of all aspects of your production, including employee training, sterility, cleanroom engineering, source and product testing and reporting, security, record-keeping, packaging and labelling…and then some!
The answer to the FAQ about GMP, “who audits GMP for pharmaceutical manufacturing and other bio-sciences/medical device manufacturing?” is as follows.
Who Audits GMP in the pharmaceutical industry?
GMP compliance is usually monitored by audits conducted by a specified Government Agency, such as the FDA, TGA, EMA, or MHRA. GMP Regulators have highly-trained GMP auditors, who often rely on PIC/S guidelines when conducting their audits of your facility, production processes, employee GMP knowledge and cleanroom validation measures.
GMP Auditors | Who governs your organization’s GMP compliance?
Lists of auditors for GMP for pharmaceutical, medical device and biomedicines manufacturing are listed below, per country.

Here are some basic facts about worldwide GMP regulatory bodies for therapeutic goods, including medicines, medical devices biomedicines and herbal supplements.
- PIC/S is described below; PIC/S lists international pharmaceutical production standards and GMP AUDIT inspection guidelines
- PIC/S (cGMP) is followed by the majority of countries producing pharmaceuticals, medical devices and other therapeutic goods
- While most countries follow PIC/S, not all countries are members — memberships are shown in the map illustration below
Why aren’t ALL countries required to follow PIC/S (GMP) for pharmaceutical or medical device manufacturing?
- If a country is exporting medicines into a country that follows PIC/S, they will usually be required to follow PIC/S (cGMP) — but not all manufacturing countries export medicines
- Some countries may not have the resources or government incentives for ensuring PIC/S is followed during pharmaceutical productions
- Other countries are currently working to improve their country’s regulatory auditing processes and manufacturing standards, so they can gain PIC/S membership status
GMP Regulation | Different countries may have a different GMP regulatory structure in relation to the manufacturing of therapeutic goods.
- Some country’s regulatory agencies focus specifically on pharmaceuticals and other therapeutic goods
- Others, like the USA’s FDA, monitor the safety of food and drugs together under one head agency (individual FDA departments handle regulatory functions for food vs drugs, but they fall under one key Government department versus two entirely independent agencies)
For example, in Australia, food production is monitored and audited separately to pharmaceutical products and other therapeutic goods, which fall under the TGA’s auditing realm.
Read about what the TGA does NOT regulate, including cosmetics and veterinary medicines GMP. However, these industries are also required to ensure GMP compliant production and distribution.
USA FDA and GMP (PIC/S) Audits
In America, these two industries (sectors) are combined in terms of GMP regulations and FDA Audits.
- In the USA, one head organisation, known as the U.S. Food and Drug Agency, monitors both FOOD (FDA food products auditing department) and DRUGS (FDA medicines and drugs auditing department)
- These departments are run as separate divisions, yet are part of the same broader agency (FDA)
Can you be audited by more than one agency or regulatory body?
- Yes, if your industry has a Governing Body (most do), they likely require industry membership
- The governing body may have auditing capacities
- You may also have State Regulators (or Federal Regulators) as well as other agencies, such as industry regulators
- Worksafe (OH&S or Workplace Safety) also has regulatory functions and can audit your site, facilities and employee training processes
It’s important to note that some industries or countries have several regulatory agencies they need to consider when it comes to GMP and PIC Scheme compliance (example: the medicinal cannabis sector)
Read on to review which agencies conduct GMP audits in different parts of the world, such as the FDA, TGA, HPFBI, MHRA,HSA and Medsafe.
Before we start, let’s clarify that we’re discussing GMP audits in relation to the PIC/S (PIC Scheme). This is what many health agencies follow in their pharmaceutical GMP audits.
What does PIC/S stand for?
PIC/S means the Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme (PIC/S).
- The Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme (PIC/S) was established in 1995 as an extension to the Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention (PIC) of 1970.
- Source: https://picscheme.org/en/picscheme
Purpose and Role of PIC/S (PIC Scheme) – Mission and Aim
- PIC/S aims at harmonising inspection procedures worldwide
- They aim to develop common standards in the field of GMP and inspections, including providing training opportunities for GMP inspectors and Regulatory Auditors to GMP businesses (Pharmaceuticals, Medical Devices, Bio-Sciences)
- Facilitates co-operation and networking in the industry (connecting experts, authorities and international organisations)
The PIC/S mission (PIC scheme mission statement): to lead the international development, implementation and maintenance of harmonised GMP standards and quality systems of inspectorates in the field of medicinal products.
Who participates in the PIC Scheme? List of participating countries for PIC/S
- Excerpt: PIC/S presently comprises 54 Participating Authorities (‘PIC/S Members) from all over the world (Europe, Africa, America, Asia and Australasia).
- A list of PIC/S members is provided below
- The map illustration also indicates current PIC/S members (Map source: https://picscheme.org/en/picscheme )
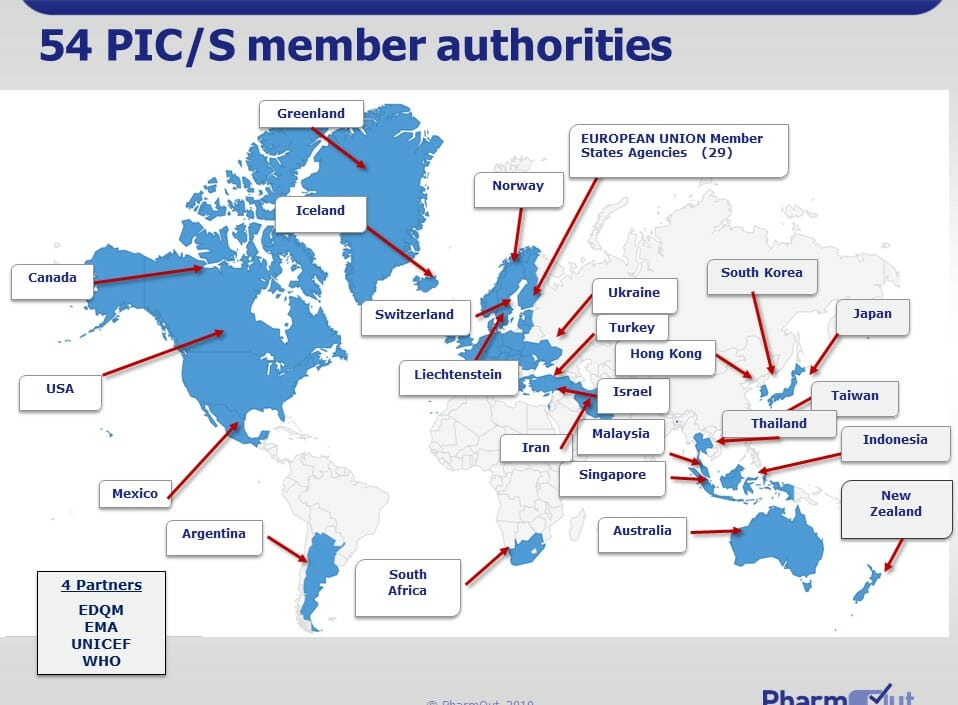
If PIC/S aim is to improve standards for worldwide GMP production and manufacturing inspections, who actually does the GMP auditing?
GMP Audits | Regulatory Auditors in different countries
Who audits GMP for pharmaceutical manufacturing, medical devices and the bio-science industry?
There are hundreds of Regulatory Authorities across the world. A large proportion of them are PIC/S members and we expect this to increase over time, as more low-income countries get involved in pharmaceutical production to increase their GNP and GDP.
These government regulatory agencies handle GMP audits for their regional organisations; e.g. audits in life sciences, radioactive medicines and bio-medicine manufacturing, medical device manufacturing, medicinal cannabis extraction / pharmaceutical-grade cannabis production, other GMP pharmaceuticals and therapeutic goods.
These Government Regulatory Agencies have highly trained Auditors who conduct frequent GMP audits against the PIC/S scheme GMP requirements.
- Each country has a different organisation (agency, monitoring group and/or health department) that monitors these production and manufacturing businesses
- Each agency will handle GMP audits and corrective measures (their employees are often highly trained to compare your procedures, systems and product testing to the PIC/S scheme guidelines)
- Depending on which PICs version your country regulatory authority refers to during inspections and site audits:
- The current PIC/s is PE-009-14 (Parts I & II) – with current updates to PIC/s Annexes dated July 2018, which went into effect in several countries as of 2020 (despite delays in implementing the most recent/current GMP regulations due to Covid restrictions – e.g. remote auditing became popular as of approximately May/June 2020)
- The recent PIC/s version is PE-009-13 (Parts I and II) dated January 2017, with PE 09-13 Annexes also of the same publication date
- It’s important to ensure your CAPA system, record-keeping, data integrity and validation processes meet the highest GMP standards and conduct regular self-inspections
In the USA, the regulatory body for medications, supplements, medical devices and other approved therapeutic goods is the FDA (The Food and Drug Administration). They handle initial applications for FDA approval as well as GMP Audits, testing and reporting requirements, as well as pharmaceutical product recalls.
Read the blog on the nature of fake medicines and fatalities related to substandard pharmaceuticals in the USA market and worldwide.
Visit the online GMP certificate courses for relevant e-learning | GMP Certificate Courses
Examples: PIC/S GMP sterile manufacturing
See more at Online training | PIC/S GMP sterile manufacturing training bundle.
This bundle includes all GMP courses relating to the manufacture of sterile final dosage medical products for a PIC/S regulated company.
Included in the bundle are:
- Module 1: Good Manufacturing Practice 01
- Module 2: Good Record-Keeping 01
- Module 3: Annex 1 – Manufacture of Sterile Medicinal Products
- Module 4: The 10 Golden Rules of GMP

Last updated on March 21st, 2024 at 06:05 am